Overview
Diamonds contains a lot of plate types. The table below gives an overview of their differences
| Icon | Which thickness bears one or two direction(s)? | Display of stresses | Reinforcement zones | Examples | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| principle
x’-direction |
secundairy
z’-direction |
||||
 (e) in two directions |
✓ | 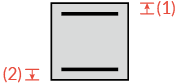 |
 |
 |
|
|
(1) in one direction |
✓ |  |
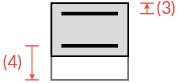 |
 |
|
|
(e) in one direction |
✓ |  |
– |  |
|
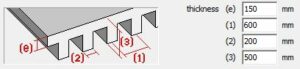 (e) in two directions (e) in two directionsthe ribs in one direction |
✗ |  |
 |
 |
|
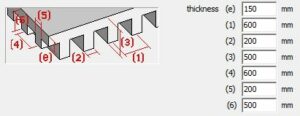 (e) in two directions (e) in two directionsthe ribs in one direction |
✗ |  |
 |
 |
|
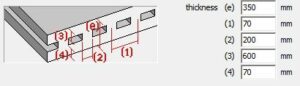
(3) and (4) in two directions |
✗ |  |
 |
– | |
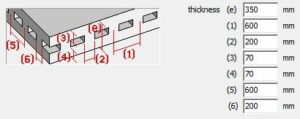 (3) and (4) in two directions (3) and (4) in two directionsthe ribs in one direction |
✗ | 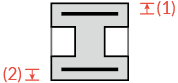 |
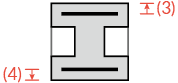 |
 |
|
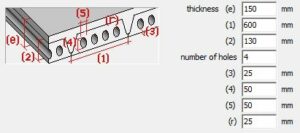 (e) in one direction (e) in one direction |
✗ | reinforcement calculation not possible |  |
||
| this plate type (a membrane) has no bending stiffness, only axial stiffness | ✓ | reinforcement calculation not possible | – | ||
| bearing direction is imposed by the user-defined stiffness matrix | ✗ | reinforcement calculation not possible |  |
||
1. The weight gain due to the holes can be compensated either by applying an up an upward load on the relevant plates or by adjusting the concrete density in the material library for the relevant plates. ↩